Trace Analysis of Iron by Sorbent Extraction
Enhancement of sensitivity gained by enrichment of target compound on a sorbent will be offset by its dilution on the way to detector, and also by its slow release from sorbent. Since column is in closest possible proximity to flowcell (1.3.14.A.), it is the rate of release of Fe(II)ferrozine from the column, that will effect sensitivity of an assay, if the volume of the flowcell will be lower than volume of eluate containing the target compound.
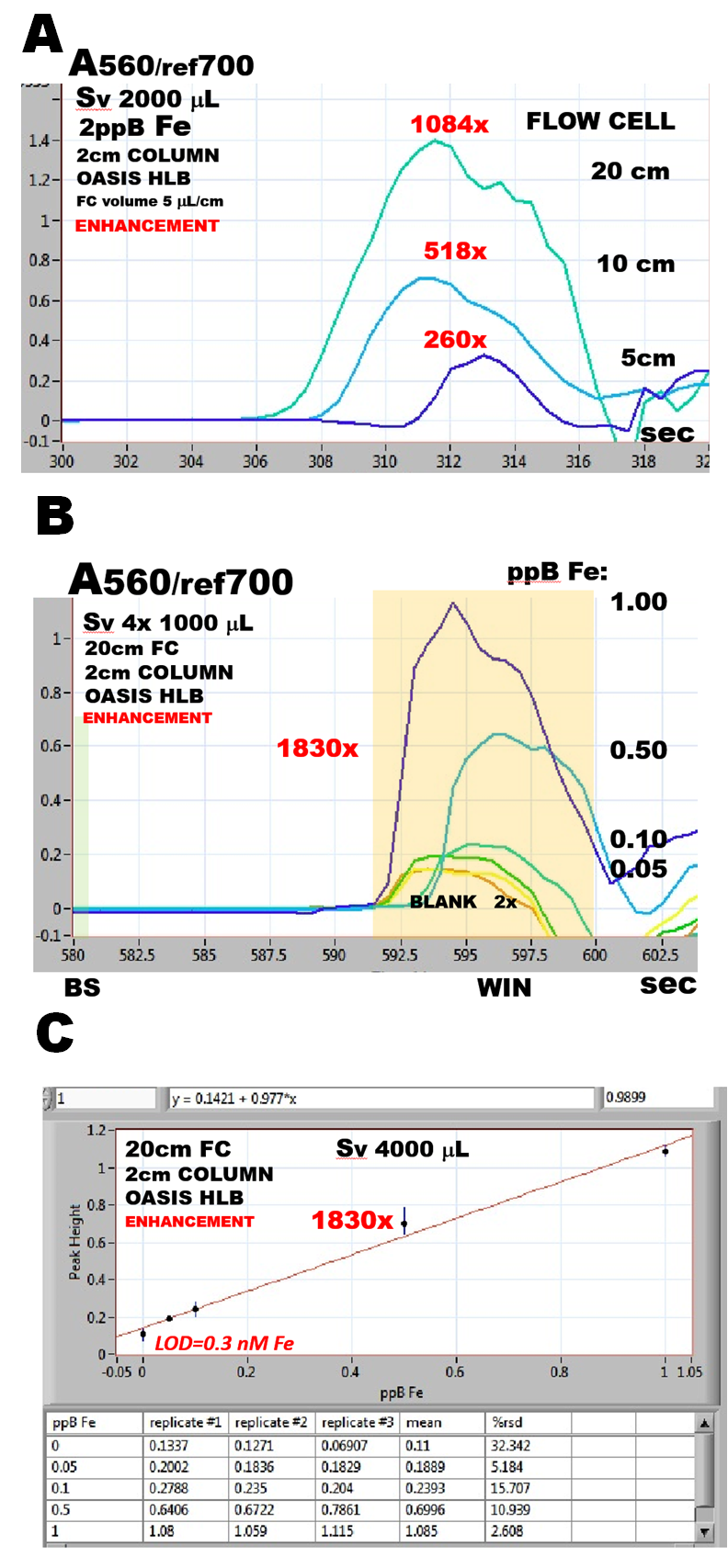
Three flow cells of increasing volumes (and light paths lengths), were used to monitor the eluted complex obtained with 2ppB Fe samples processed by assay protocol (1.3.14.B fig.C), adjusted to two injections (Sv 2000 mcrL), (A). Since the light path of these flowcells is constructed from 0.8mmI.D. PEEK tubing (for details see 2.3.6.) their internal volumes were 25, 50 and 100 mcrL. It was found that response increased linearly up to 20 cm long flow cell, because gradually eluted complex filled entirely even the longest flow cell. (A eluant flowrate 4mcrL/sec))
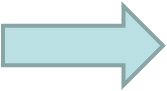
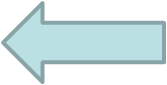
Sensitivity of SE based assay performed in programmable FI format is therefore determined by combination of the length of the light path of a flowcell and of the volume of processed sample. By using protocol (1.3.14.B.) adjusted to Sv 4000mcrL with 20 cm long flow cell, and eluant flowrate of 10mcrL/s (B), the sensitivity of the method was enhanced 1830x compared to conventional colorimetry using 1 cm long flow cell (C).
Limit of detection of 0.3nM Fe achieved by this protocol (C), is significant, but can be viewed only as an estimate of the ultimate LOD of SEpFI based assay, because, the sample processing frequency, - only 5 measurements per hour (B) is impractical for real life applications.
Furthermore, value of blank, due to contamination of reagents by iron, is artificially low in these experiments, because reagent contribution to blank was diluted along with Fe(II) ferrozine complex, when preparing standards by serial dilution. Automation of the entire assay protocol, including formation of Fe(II) ferrozine was investigated, and the results are discussed on the following pages.
1.3.14.C.